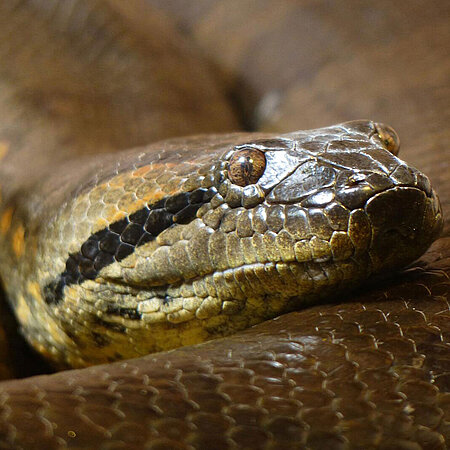
Green Anaconda
Eunectes murinus

- FamilyBoas (Boidae)
- Length3 – 8 m
- HabitatWetlands, seasonal flooded grasslands
Suffocating prey
Instead of hunting, they lie in wait for their prey. When a victim approaches, they strike with lightning speed, seizing it with their sharp, curved teeth. The snake then coils its body around the prey’s ribcage and constricts, causing gradual but certain suffocation. Juvenile green anacondas mainly eat birds and small caimans, while adult prefer larger animals such as capybaras.
Fasting period
During the 7-month gestation period, the female eats nothing at all. Green anacondas produce between 20 and 40 eggs in the womb and give birth to live young. The neonates (baby snakes) are ca. 70 cm long and weigh ca. 200 g. However by the time they are fully grown their weight will increase a thousand-fold.
The green anaconda is the world’s largest constrictor and the longest animal at Hellabrunn Zoo.
Distribution