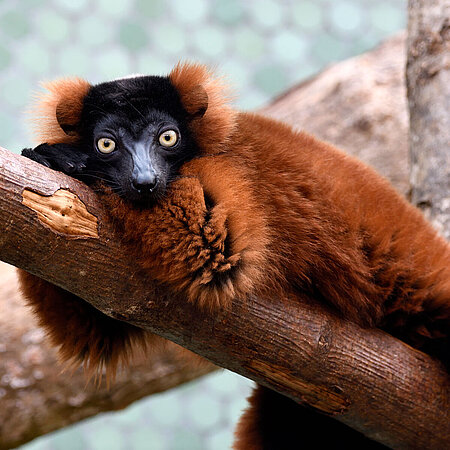
Red ruffed lemur
Varecia rubra

- Family
- Strepsirrhine primates (Lemuridae) (Lemuridae)
- Weight
- 3,5 – 4 kg
- Habitat
- primary rainforests
Loud concerts
Red ruffed lemurs communicate using up to twelve different calls. The loud calls can be heard by the farthest group members and are used to keep the group together when foraging or to warn others of predators. Individual groups also organise regular “concerts” for territorial expression. Red ruffed lemurs can even understand the calls of black-and-white lemurs, which are found in a different part of Madagascar.

Nest at dizzy heights
Female red ruffed lemurs typically give birth to two to three infants. For the fi rst few weeks, the mother leaves her young in a well-constructed nest 10 – 20 m above the ground whenever she forages for food, returning only to suckle and sleep. During her absence, the group will keep an eye on the little ones, particularly as accidental falls are usually fatal.
Basis of Life
The red ruffed lemur has a thick coat of fur to protect it from heavy rain, which is common in Madagascar, the only area in the world where it is found.
Distribution

Hellabrunn Zoo participates in the European Endangered Species Programmes